자료의 형태별로 함수에 인자를 전달하는 방법을 정리해본다.
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int TestFuncBasic(int arg1, int arg2);
void TestFuncPointer(int arg1, int* arg2);
void TestFuncReference(int arg1, int& arg2);
void TestFuncArray(char arg[]);
void TestFuncMultiArray(int arg1[][2], int arg2[][2][2]);
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
// Ex1> basic : 변수를 전달하고 리턴을 받는다.
int valueBasic1 = 100;
int valueBasic2 = 100;
int valueBasicReturn;
valueBasicReturn = TestFuncBasic(valueBasic1, valueBasic2);
cout << "Ex1> " << valueBasicReturn << "\n";
// Ex2> pointer : 변수와 포인터를 전달하고 포인터를 활용해 계산된 값을 읽는다.
int valuePointer1 = 100;
int valuePointerReturn = 0;
int* valuePointer2 = &valuePointerReturn;
TestFuncPointer(valuePointer1, valuePointer2);
cout << "Ex2> " << valuePointerReturn << "\n";
// Ex3> reference : 변수를 전달하고 참조를 이용해 계산된 값을 읽는다.
int valueReference1 = 100;
int valueReference2 = 100;
TestFuncReference(valueReference1, valueReference2);
cout << "Ex3> " << valueReference2 << "\n";
// Ex4> array : 배열 전달하고 참조를 이용해 수정된 값을 읽는다.
// ※ 실제로는 포인터를 전달함에 유의할것
char valueArray[100] = "Array Tast";
TestFuncArray(valueArray);
cout << "Ex4> " << valueArray << "\n";
// Ex5> array : 다차원 배열 전달시에는 맨앞쪽 대괄호를 비워둔다.
int multiArray1[2][2] = {
{ 1, 2 },
{ 3, 4 }
};
int multiArray2[2][2][2] = {
{
{ 1, 2 },
{ 3, 4 }
},
{
{ 5, 6 },
{ 7, 8 }
}
};
TestFuncMultiArray(multiArray1, multiArray2);
cout << "Ex5> " << multiArray1[0][0] << " // " << multiArray2[0][0][0] << "\n";
return 0;
}
int TestFuncBasic(int arg1, int arg2)
{
return arg1 + arg2;
}
void TestFuncPointer(int arg1, int* arg2)
{
*arg2 = arg1 + 100;
}
void TestFuncReference(int arg1, int& arg2)
{
arg2 = arg1 + 100;
}
void TestFuncArray(char arg[])
{
arg[7] = 'e';
}
void TestFuncMultiArray(int arg1[][2], int arg2[][2][2])
{
arg1[0][0] = 2;
arg2[0][0][0] = 2;
}
함수에 인자를 전달함에 있어 메모리가 어떻게 운영되는지 유념할 필요가 있다.
Ex1>방식의 경우 전달 하고자하는 인자와 함수에서 전달받은 인자를 저장하는 부분에서 메모리를 2배로 사용하게 되어 성능상의 불리한 점이 있다.
다음 그림을 참고하도록 한다.
Ex1>

* main에서는 valueBasic1, valueBasic2, valueBasicReturn 세개의 값이 메모리를 차지하고 있다.
* TestFuncBasic를 호출하면 arg1, arg2가 메모리에 올려지고 계산된 값을 반환함과 동시에 소멸된다.
Ex2>
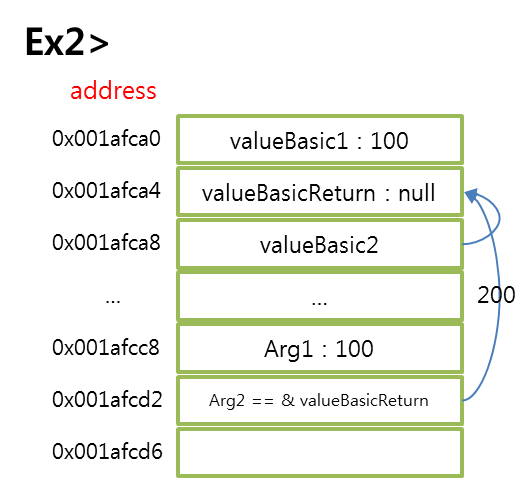
* main에서는 valueBasic1, *valueBasic2, valueBasicReturn 세개의 값이 메모리를 차지하고 있다.
* 포인터변수 *valueBasic2는 valueBasicReturn의 주소값을 가지고 있다.
* 함수를 호출하면 전달된 포인터변수가 가리키는 값에 계산결과를 넣는다.

